What is the gallbladder, and what function does it serve?
Introduction: Looking like a pear, the gallbladder is a little organ in the upper right of the belly. It resides under the liver. Store and concentrate the bile the liver generates, a digestive fluid required for the breakdown and absorption of dietary fats. The strong bladder channels food containing fat before sending it along with bile to the duodenum. The duodenum, the first part of the small intestine, further breaks down food and absorbs nutrients. This convoluted procedure emphasises the gallbladder’s importance in your diet. The gallbladder’s location in the body helps it to cooperate closely with the stomach and liver. The gallbladder fills when the liver constantly generates bile, not immediately needed for digestion. By generating a concentrated amount of bile during digestion, this organ acts as a strong reservoir, helping the body to readily break down fatty foods. Made from bile salts, cholesterol, and bilirubin (a yellow material created when red blood cells break down), bile’s main purpose is to break down fat molecules into smaller, water-soluble droplets so that they can be digested and absorbed. Strong emulsifiers bind lipids firmly, facilitating easier absorption. Control of blood flow depends critically on the gallbladder.

The strong sphincter of Oddi is a muscle valve at the beginning of the small intestine.
It controls the flow of pancreatic and bile fluids into the small intestine, which determines when bile can come out. This method ensures the release of bile only when necessary, thereby avoiding the waste of this essential substance. Gallstones or inflammation might compromise gallbladder capacity, thereby causing digestive problems and maybe pain. People who are familiar with the gallbladder’s structure and activity will be able to appreciate its importance for digestive health and grasp the consequences of gallbladder issues. Typical Gallbladder Issues: How They Show Up An essential component of the digestive process, the gallbladder stores bile the liver generates—needed for the breakdown of fat. Several disorders can damage this organ, leading to major medical complications. Powerful gallstones and strong cholecystitis are disorders that result in red, enlarged, and irritated gallbladders. Gallstones come in various diameters. Made from either bile cholesterol or bilirubin, gallstones are brittle lumps. Though they may not show any symptoms, when they do, usually they have extreme pain in the upper right abdomen together with nausea and vomiting. Eating fatty foods increases the effort your liver makes, which can lead to these symptoms. Conversely, gallstones usually aggravate liver inflammation in those suffering from cholecystitis. Blocked bile ducts can produce jaundice, fever, and extreme stomachache. The fact that the pain of this disorder starts fast and gets worse in a few hours distinguishes it. Furthermore, some people could experience continuous pain that interferes with their regular activities. Still, another major problem is bile duct blockage. Gallstones, tumors, or strictures are just a few of the several causes this can have. Some of the symptoms are dark urine, itching, bile accumulation, and pale stools since this blockage results in them. Early identification of these symptoms is crucial for effective treatment, as, in the case of long-lasting obstruction, liver damage may be reversed. If you have gallbladder issues, pay attention to any symptoms that linger since they could indicate more major issues. Those with severe discomfort, with a fever, or who have observed changes in their skin tone should consult a doctor immediately to prevent long-term medical issues.How to Managing Stress: Simple Strategies for Your Daily Life
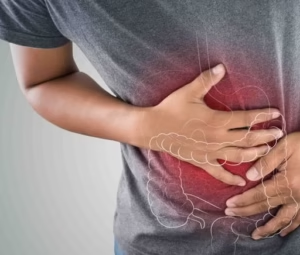
Learning about the symptoms and causes of this gallbladder.
Issues will enable individuals to maintain their health actively. A gallbladder diagnosis calls for several tests and procedures. The health of the gallbladder depends on its being free from problems. We can evaluate gallbladder performance, spot blockages, and hunt any disorders using a range of tests and techniques. Usually, the first components of an initial assessment are a physical check and a complete medical history. To find the state of the gallbladder, we next run imaging and functional testing. One common approach to identifying problems is via ultrasonic tests. Usually, the first test is A thorough physical examination and a detailed medical history initiates the gallbladder assessment journey, establishing the foundation for a precise diagnosis. After this first checkup, more advanced imaging methods and functional tests are essential for finding out what’s wrong with the gallbladder. Ultrasonic tests are becoming the best way to find problems. Notably, subsequent assessments and treatment plans often heavily rely on the results of the initial test. By integrating these comprehensive approaches, healthcare professionals can ensure a more precise.

Understanding of gallbladder health,
ultimately leading to better patient outcomes, is a painless one.
Professionals observe images of the gallbladder created by sound waves throughout this procedure. This clarifies gallstones, inflammation, or other issues for them. One should expect this test to last roughly thirty minutes. They might have to fast before the exam to enable the gadget to see clearly. Hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA): A scan with a radioactive tracer is another important way to measure how much the gallbladder can store and empty. This operation evaluates the performance of the gallbladder and exposes disorders like cholecystitis, a condition marked by gallbladder inflammation. Depending on the protocol, individuals might feel some discomfort during the one- to four-hour test. Endoscopic methods such as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) allow doctors to diagnose conditions as well. These are very useful for inspecting the gas ducts. This approach passes a flexible tube with a camera via the mouth into the upper digestive tract. This approach not only identifies the problem but also has the possibility of fixing it using bile canal stone removal. This procedure will induce sedation in patients, thereby enhancing their comfort during the test. Using their understanding of the test results, healthcare professionals can recommend the best approaches to patient treatment. Should the tests show that the gallbladder is dysfunctional, especially in cases of ongoing symptoms or issues, surgery could be a reasonable choice. Important testing will help to ascertain whether major gallbladder issues call for a cholecystectomy—that is, gallbladder removal. Gallbladder issues have treatments and answers at hand. Based on how severe the gallbladder issue is and what type of problem it is, there are several approaches to treating gallbladder issues, ranging from minor lifestyle adjustments to more involved operations. Those suffering from gallbladder issues, including heartburn, bloating, or pain, can initially consider non-invasive techniques.

Keeping your gallbladder healthy mostly depends on changing your diet.
Your symptoms will improve much if you cut processed meals and high-fat items from your diet and replace them with lean meats and healthy fats. Whole grains, veggies, and fruits assist your body in breaking down meals and reduce your risk of liver issues. Furthermore, adequate water is crucial since it facilitates the proper operation of the digestive tract. For some people’s symptoms or particular issues, such as gallstones, doctors could write prescriptions for medications. For those who are unable to undergo surgery, bile acid medications can help eliminate cholesterol gallstones. Not everyone will benefit from this medication, and its effects could take months. Should gallbladder issues continue or get worse, doctors may advise surgical treatment—more especially, a cholecystectomy. Usually carried out laparoscopically, this procedure eliminates the gallbladder to hasten patient recovery. Those unable to have surgery could have bile duct obstructions cleared using other techniques, such as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). Gallbladder health is still a major component of overall health; hence, it is crucial to discuss your particular needs with a doctor to receive the best therapy. New medicines and continuous gallbladder problem studies reveal how shifting care decisions are. This emphasizes how crucial early identification and aggressive treatment are for achieving optimal health results.How to Making small changes to live a healthier life
Note:
Above article for your general knowledge.If you have this kind of issue, please consult a doctor.
RELATED POSTS
View all


